cervical spine tests foraminal compression distraction valsalva|cervical distraction test results : private label The cervical spine, the uppermost portion of the spine, is made up of 7 cervical vertebrae. Between these vertebrae project the trunks of the 8 pairs of cervical nerve roots. There are a number of special tests for the cervical region that asses both the mobility of the spine as well as the compromise of the nerves and vessels in the area.
O Confiança iniciará a rodada estando bastante próximo à zona de classificação à próxima fase da Série C do Brasileirão 2023. Entretanto, de jeito maneira, dá . Ver mais
{plog:ftitle_list}
Jogos elegíveis são exibidos na guia à esquerda destes termos. As apostas em alguns de nossos jogos não contam por inteiro para . Ver mais
A systematic review of six studies showed that in patients without neurologic deficits, positive results on the Spurling test, neck distraction test, and Valsalva test (each with.Neural foramen and joint capsules around the facet joints of the cervical spine are tested during the Cervical Distraction Test. The neck extensor muscles are also secondarily observed . Chance Fracture (flexion-distraction injury) . cervical spine C6 nerve root travels under C5 pedicle (mismatch) . foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed .
Valsalva test is used widely with different specialties and has different instruments and different applications according to the field and the target it is used for. . Allison S. Reliability and diagnostic accuracy of the clinical .
neural foramen neck test
(2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients .The cervical spine, the uppermost portion of the spine, is made up of 7 cervical vertebrae. Between these vertebrae project the trunks of the 8 pairs of cervical nerve roots. There are a number of special tests for the cervical region that asses both the mobility of the spine as well as the compromise of the nerves and vessels in the area.Rubinstein et al. completed a systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of physical exam tests for cervical radiculopathy. It was concluded that Spurling, neck distraction, Valsalva and upper limb tension tests are most useful in establishing a diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy in patients without neurological deficits.neck pain with radiating pain/cervical radiculopathy, including the upper limb tension test, Spurling's test, distraction test, and the Valsalva test. Cranial cervical flexion and neck flexor muscle endurance tests may be use in assessing movement coordination impairments, and algometric assessment of pressure pain threshold may be useful in .
You may hear your provider refer to the Spurling test as the maximal cervical compression test or foraminal compression test. This may sound like a formal test, but you can think of it as a physical exam to assess neck pain. . Cervical spine instability. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy. A recent spine injury. Rheumatoid arthritis. Metastasis . Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single cervical nerve root. It is caused by nerve root compression in the cervical spine either from degenerative changes or from an acute soft disc hernation.- tests for cervical nerve root compression - pt is seated, lateral flexion of the c-spine with axial loading - positive if symptoms are replicated (n/t) and relieved with distraction - tests for nerve root compression - active neck flexion - positive if symptoms are replicated (burning sensation into the extremities)
Cervical spine 1. PROM a. Overpressure tests 2. Neurologic a. Foraminal compression (Spurling’s) test b. Distraction test c. Upper limb neurodynamic (tension) test (brachial plexus tension test or Elvey test) d. Bickle’s sign – ULTT 4 done actively e. Brachial plexus tension test f. Brachial plexus provocation test g."Cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. This impingement typically produces neck and radiating arm pain or numbness, sensory deficits, or motor dysfunction in the neck and upper extremities.". Cervical radiculopathy occurs with pathologies that cause symptoms on the nerve roots. Cervical radiculopathy is a substantial cause of disability and morbidity [], and is a common condition, affecting both sexes after middle age [].Cervical radiculopathy refers to those subjects with signs and symptoms related to dysfunction of the spinal nerve root(s) of the neck [].The diagnostic criteria are, however, unclear [7, 43].Some suggest that cervical .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Test: Foraminal Compression Whats being tested: Patient position: Positive finding:, Test: Distraction Test Whats being tested: Patient position: Positive finding:, Test: Shoulder Abduction Test Whats being tested: Patient position: Positive finding: and more.Compression of the cervical nerve root may occur due herniation of disk material or bony osteophytes that impinge on the cervical nerve root. . the shoulder abduction test, Valsalva maneuver, Neck distraction, and Elveys upper limb tension . Haig AJ, Yamakawa K. The spurling test and cervical radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2002;27:156 .
Spurling Test (Foraminal Compression Test . Osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis or cervical spine instability. Foraminal Distraction Test . Valsalva Maneuver. Valasalva Maneuver Effects During Strenuous Lifting (FYI) Swallowing Test Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Foraminal compression, Distraction test, Shoulder ABduction test and more. Scheduled maintenance: June 29, 2024 from 11:00 PM to 12:00 AMThe Cervical Distraction Test also called Traction/Distraction test is a symptom-relief test to assess for cervical radicular syndrome/cervical radiculopathy. It has been described to have a sensitivity of 44% and a high .
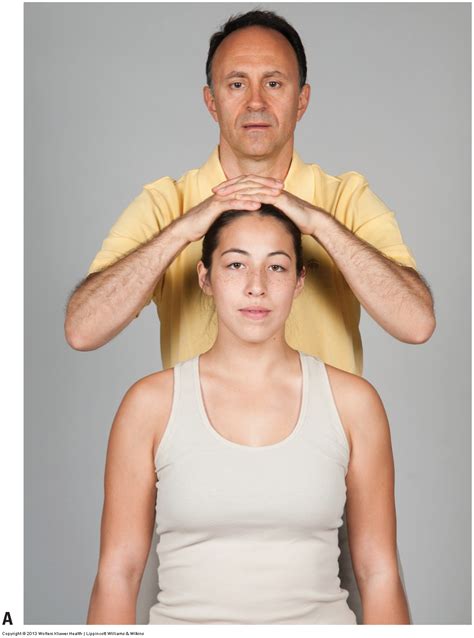
Foraminal Distraction Test 1) Patient is sitting on stool 2) Clinician applies distraction force by one hand cupping the chin (mastoid process) and one hand on back of head 3) Positive test -> •Reduction of symptoms/pain = nerve root impingement •Pain gets worse = muscular or ligamentous injury 4) Indication -> •Nerve root impingement . Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Test: Foraminal Compression What's being tested: Patient position: Procedure: Positive finding:, Test: Distraction Test What's being tested: Patient position: Procedure: Positive finding:, Test: Shoulder Abduction Test What's being tested: Patient position: Procedure: Positive finding: .
Spurling Test (Foraminal Compression Test . Osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis or cervical spine instability. Foraminal Distraction Test . Valsalva Maneuver. Valasalva Maneuver Effects During Strenuous Lifting (FYI) Swallowing TestPalpation Test. Section 2: Cervical Spine. Vertebral Artery Test. Foraminal Compression Test (Spurling) Foraminal Distraction Test. Valsalva’s Maneuver Swallowing Test Tinel’s Sign. Section 3: Shoulder Empty Can (Supraspinatus) Test. .
Some previous reviews have summarized the results of studies on the diagnostic accuracy of the physical examination for the identification of cervical radiculopathy [8–10,15,16].Two reviews included an assessment of the methodological quality of the primary studies and one review offered a qualitative summary of the findings .These reviews noted that some provocative .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Rust Sign, Foraminal Compression, Max Foraminal Compression and more. . UPPER CERVICAL SPINE FRACTURE. Click the card to flip 👆 . Cervical Distraction. CERVICAL NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION. Shoulder Depression.Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a neck condition that arises when the spinal cord becomes compressed — or squeezed — due to the wear-and-tear changes that occur in the spine as we age. Although the condition commonly occurs in patients over the age of 40, it can occur in younger people who were born with narrower spinal canals.Foraminal Compression Jackson's Compression Extension Compression Flexion Compression . Isolates the cervical spine during passive neck flexion . Distraction Test 1) Diagnosis 2) Biomechanical mechanism 3) Positive Sign. .It is important to remember that this test alone does not have high diagnostic accuracy and should be clustered with other tests (check out the Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint Homepage!). Note: tests should only be performed by a properly trained health care practitioner.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What are the tests for spinal cord and meningeal testing?, L'Hermitte Sign Positive, L'Hermitte Sign Indicator and more. . jackson compression, maximal cervical compression, valsalva maneuver, cervical distraction test, bakody sign. soto-hall positive. generalized pain in the .
neural foramen neck distraction
conclusion of hardness test
cervical distraction test results
30K Followers, 2,009 Following, 257 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Giulia Martins (@giuliasmartins)
cervical spine tests foraminal compression distraction valsalva|cervical distraction test results